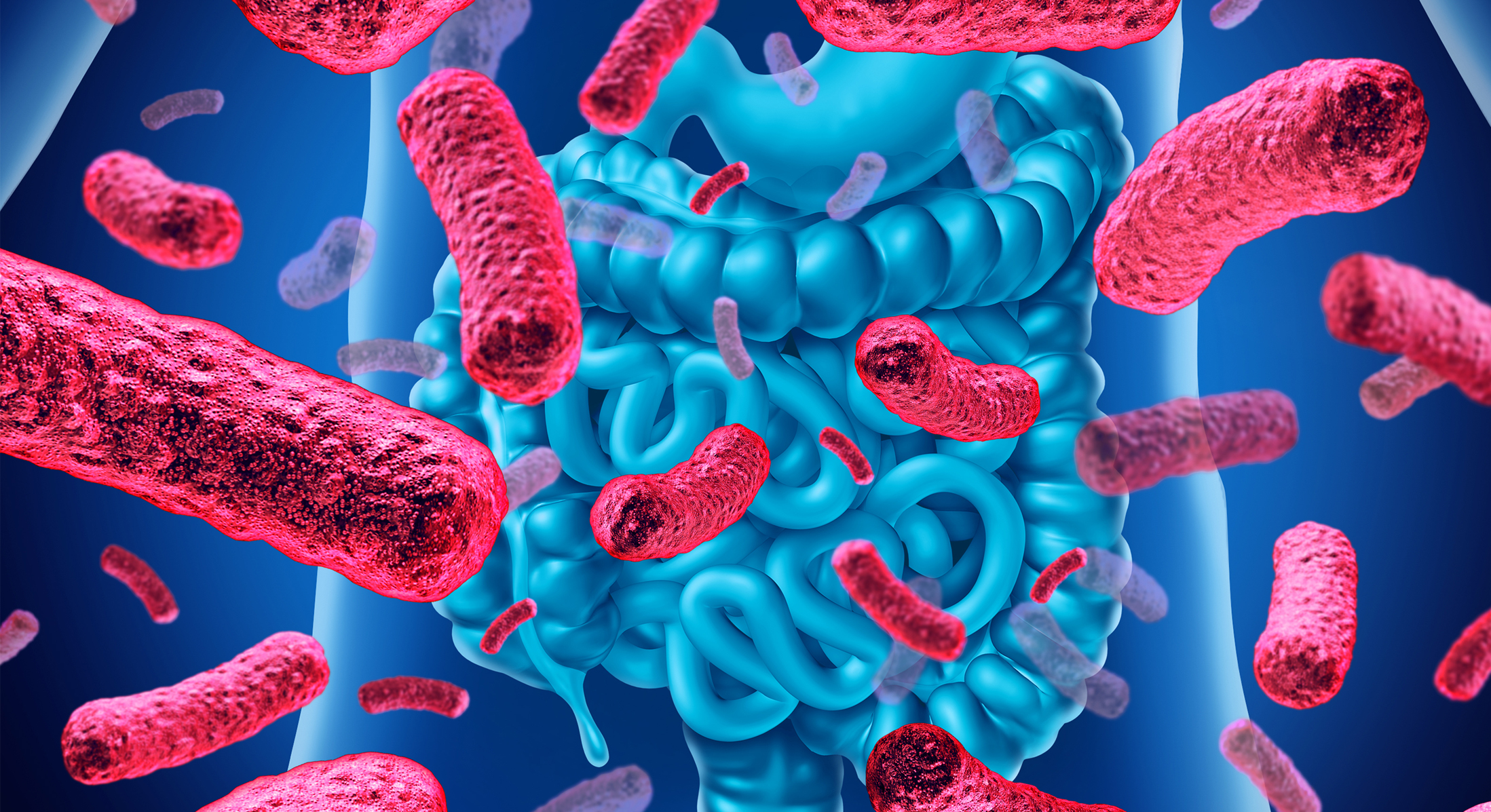
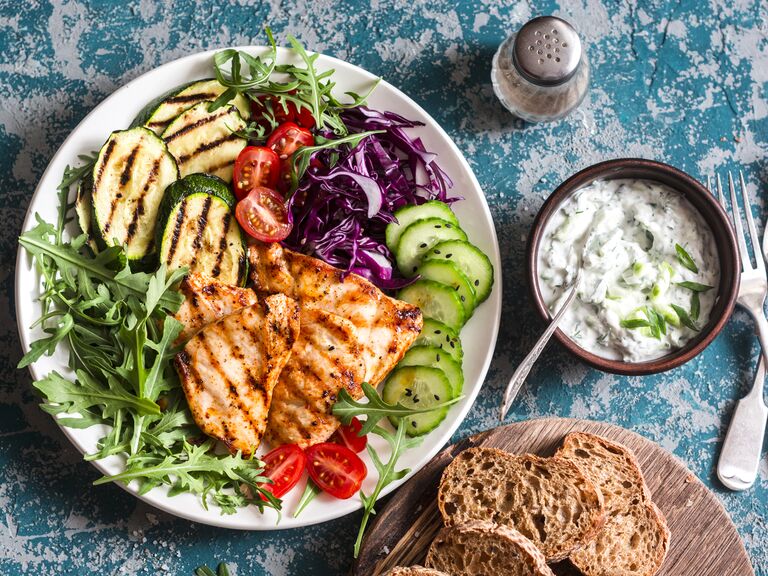For years the Mediterranean Diet has been considered the one of the healthiest diets on the planet. With a foundation based on vegetables, fruit, nuts, whole grains, and limited quantities of meat—it has often been praised for its all-around health benefits.
Inspired by the eating habits of the Greeks, the diet has been proven to be an effective dietary choice for individuals aiming to live a long, healthy life. Areas around the world with the longest expected life spans or “blue zones,” all tend to follow some variation of the Mediterranean Diet.
In addition to the previously realized health benefits, new findings have suggested that the Mediterranean Diet may also help improve the gut microbiome. A recent study published found that following the diet for a single year may help improve cognitive function while aiding in longevity (1).
Hi, I’m Sean Torbati. Aging is an inevitable part of human existence. As we get older our bodies change—the good news is there are steps we can take to age in a more graceful manner. Following a well-rounded diet such as the Mediterranean Diet is one way we can increase our longevity.
Let’s take a look at how the diet can improve your health by altering the gut microbiome.
What is the Mediterranean Diet?
As the name suggests, the Mediterranean Diet focuses on a high intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans, legumes, and occasional fish and poultry options. As a nutritionally sound dietary option it offers an eclectic array of food choices seasoned with various herbs and spices.
Some of the benefits of the Mediterranean Diet include:
- Reduced risk of developing diabetes (2)
- Prevention of cardiovascular disease (3)
- Improved longevity (4)
- Improved weight management (5)
One new study suggests that the health benefits of the Mediterranean Diet may be more profound than previously thought. Adherence to the diet may actually slow down the aging process by way of altering the gut microbiome.
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Aging
Since the dawn of time, aging has been associated with the deterioration of bodily functions and inflammation which causes individuals to become frail as they age. While many studies focus upon the role of aging in relation to the host organism—newer research suggests microbiota may play a critical role in aging (6).
The Relationship Between the Mediterrean Diet and the Gut Microbiome
A newly published study details how the Mediterranean Diet can alter the gut microbiome and in turn help to reduce frailty due to aging. The study looked at the gut microbiota in 612 non-frail or pre-frail subjects across five nations—United Kingdom, France, Netherlands, Italy, and Poland—before and after practicing the Mediterranean Diet for a period of one year (1).
Upon following the diet, specific microbiome alterations were noted. The findings support the idea that an improved diet can help to modulate gut microbiota while in turn promoting healthier aging.
Some of the findings of the study include (1):
- Enriched taxa
- Lower markers of frailty
- Improved cognitive function
- Negative association with inflammatory markers of C-reactive protein and interleukin-17
Analysis of inferred microbial metabolite profiles indicate that the microbiome changes were due to increases in short/branch chain fatty acid production along with lower production of secondary bile acids, p-cresols, ethanol, and carbon dioxide. Microbiome analysis showed that bacterial taxa responded positively to the Mediterranean Diet as a whole.
Although the study mainly focused upon elderly patients, other studies have also shown the diet to have similar benefits to all age groups. Another recent study noted that a Mediterranean Diet can positively impact metabolic health, gut microbiome, and improve lifestyle risk factors. Individuals that switched to a Mediterranean Diet while keeping energy intake constant experienced a reduction of blood cholesterol along with improved microbiome indicators (7). Other studies have also suggested the Mediterranean Diet to be associated with longer telomere length—a biomarker of aging (8).
Can the Mediterranean Diet Slow Down Aging?
Although some of the findings remain in their infantile stages—recent research has suggested the Mediterranean Diet has an array of health benefits. Along with improved cardiovascular function, reduced risk of diabetes, and more—following the diet may also help to improve the aging process.
While the human race is unable to stop aging, several steps can be taken to slow it down. Following a healthy diet, participating in regular exercise, and having a positive mindset can greatly impact how we age at both a physical and mental level.
Let’s age gracefully together—one day at a time. If you have any other questions about how you can improve the aging process, feel free to reach out to me. I’m here to help you age like fine wine.
Kindest regards,
Sean Torbati - PN Certified Nutritionist | EXOS Phase 3 Training Specialist
Co-Founder, Ambrosia Collective
References:
- https://gut.bmj.com/content/early/2020/01/31/gutjnl-2019-319654
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2427084/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6471908/
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Effie_Vasilopoulou/publication/12090631_Mediterranean_diet_and_longevity/links/00b4951e39aed3d079000000.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5916888/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31487470
- https://gut.bmj.com/content/early/2020/02/18/gutjnl-2019-320438
- https://www.bmj.com/content/349/bmj.g6674